This page was generated from
examples/ConsLaborModel/LaborIntMargConsumerType.ipynb.
Interactive online version: .
Download notebook.
.
Download notebook.
Interactive online version:
Intensive Margin Labor Supply Choice#
[1]:
from time import process_time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from HARK.ConsumptionSaving.ConsLaborModel import (
LaborIntMargConsumerType,
init_labor_lifecycle,
)
[2]:
mystr = lambda number: f"{number:.4f}" # Format numbers as strings
[3]:
do_simulation = True
[4]:
# Make and solve a labor intensive margin consumer i.e. a consumer with utility for leisure
LaborIntMargExample = LaborIntMargConsumerType(verbose=0)
LaborIntMargExample.cycles = 0
C:\Users\Matthew\Documents\GitHub\HARK\HARK\ConsumptionSaving\ConsLaborModel.py:147: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in divide
* (bNrmGridTerm / (WageRte_T * TranShkGridTerm) + 1.0),
C:\Users\Matthew\Documents\GitHub\HARK\HARK\ConsumptionSaving\ConsLaborModel.py:147: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
* (bNrmGridTerm / (WageRte_T * TranShkGridTerm) + 1.0),
C:\Users\Matthew\Documents\GitHub\HARK\HARK\rewards.py:65: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in power
return c**-rho
[5]:
t_start = process_time()
LaborIntMargExample.solve()
t_end = process_time()
print(
"Solving a labor intensive margin consumer took "
+ str(t_end - t_start)
+ " seconds.",
)
Solving a labor intensive margin consumer took 0.96875 seconds.
[6]:
t = 0
bMin_orig = 0.0
bMax = 20.0
[7]:
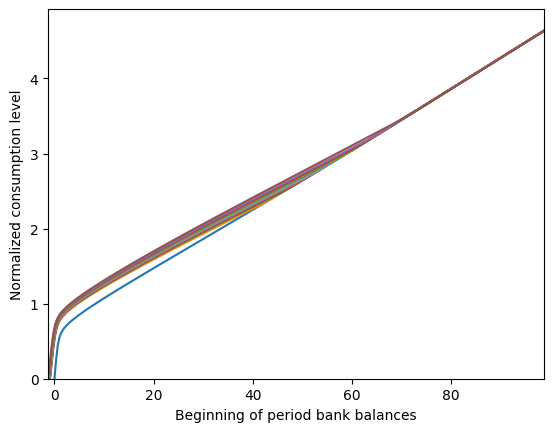
# Plot the consumption function at various transitory productivity shocks
TranShkSet = LaborIntMargExample.TranShkGrid[t]
bMin = bMin_orig
B = np.linspace(bMin, bMax, 300)
bMin = bMin_orig
for Shk in TranShkSet:
B_temp = B + LaborIntMargExample.solution[t].bNrmMin(Shk)
C = LaborIntMargExample.solution[t].cFunc(B_temp, Shk * np.ones_like(B_temp))
plt.plot(B_temp, C)
bMin = np.minimum(bMin, B_temp[0])
plt.xlabel(r"Beginning of period bank balances $b_t$")
plt.ylabel(r"Normalized consumption level $c_t$")
plt.xlim(bMin, bMax - bMin_orig + bMin)
plt.ylim(0.0, None)
plt.show()
[8]:
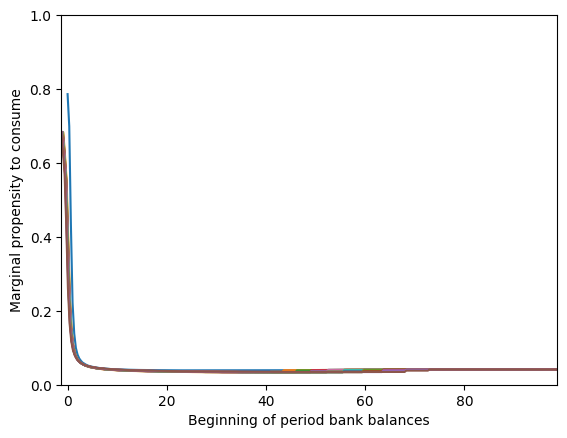
# Plot the marginal consumption function at various transitory productivity shocks
TranShkSet = LaborIntMargExample.TranShkGrid[t]
bMin = bMin_orig
B = np.linspace(bMin, bMax, 300)
for Shk in TranShkSet:
B_temp = B + LaborIntMargExample.solution[t].bNrmMin(Shk)
C = LaborIntMargExample.solution[t].cFunc.derivativeX(
B_temp,
Shk * np.ones_like(B_temp),
)
plt.plot(B_temp, C)
bMin = np.minimum(bMin, B_temp[0])
plt.xlabel(r"Beginning of period bank balances $b_t$")
plt.ylabel(r"Marginal propensity to consume")
plt.xlim(bMin, bMax - bMin_orig + bMin)
plt.ylim(0.0, 1.0)
plt.show()
[9]:
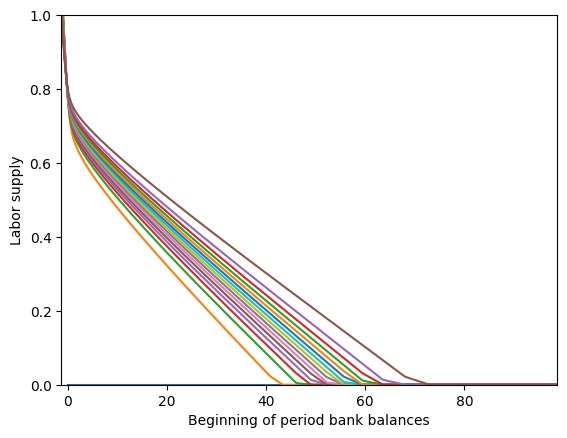
# Plot the labor function at various transitory productivity shocks
TranShkSet = LaborIntMargExample.TranShkGrid[t]
bMin = bMin_orig
B = np.linspace(0.0, bMax, 300)
for Shk in TranShkSet:
B_temp = B + LaborIntMargExample.solution[t].bNrmMin(Shk)
Lbr = LaborIntMargExample.solution[t].LbrFunc(B_temp, Shk * np.ones_like(B_temp))
bMin = np.minimum(bMin, B_temp[0])
plt.plot(B_temp, Lbr)
plt.xlabel(r"Beginning of period bank balances $b_t$")
plt.ylabel(r"Labor supply $\ell_t$")
plt.xlim(bMin, bMax - bMin_orig + bMin)
plt.ylim(0.0, 1.0)
plt.show()
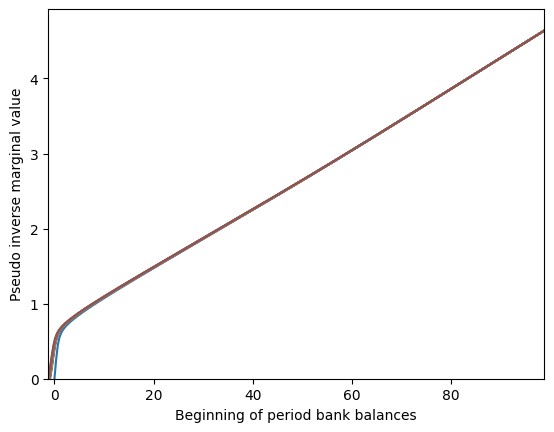
[10]:
# Plot the marginal value function at various transitory productivity shocks
pseudo_inverse = True
TranShkSet = LaborIntMargExample.TranShkGrid[t]
bMin = bMin_orig
B = np.linspace(0.0, bMax, 300)
for Shk in TranShkSet:
B_temp = B + LaborIntMargExample.solution[t].bNrmMin(Shk)
if pseudo_inverse:
vP = LaborIntMargExample.solution[t].vPfunc.cFunc(
B_temp,
Shk * np.ones_like(B_temp),
)
else:
vP = LaborIntMargExample.solution[t].vPfunc(B_temp, Shk * np.ones_like(B_temp))
bMin = np.minimum(bMin, B_temp[0])
plt.plot(B_temp, vP)
plt.xlabel(r"Beginning of period bank balances $b_t$")
if pseudo_inverse:
plt.ylabel("Pseudo inverse marginal value")
else:
plt.ylabel("Marginal value")
plt.xlim(bMin, bMax - bMin_orig + bMin)
plt.ylim(0.0, None)
plt.show()
[11]:
if do_simulation:
t_start = process_time()
LaborIntMargExample.T_sim = 120 # Set number of simulation periods
LaborIntMargExample.track_vars = ["bNrm", "cNrm"]
LaborIntMargExample.initialize_sim()
LaborIntMargExample.simulate()
t_end = process_time()
print(
"Simulating "
+ str(LaborIntMargExample.AgentCount)
+ " intensive-margin labor supply consumers for "
+ str(LaborIntMargExample.T_sim)
+ " periods took "
+ mystr(t_end - t_start)
+ " seconds.",
)
N = LaborIntMargExample.AgentCount
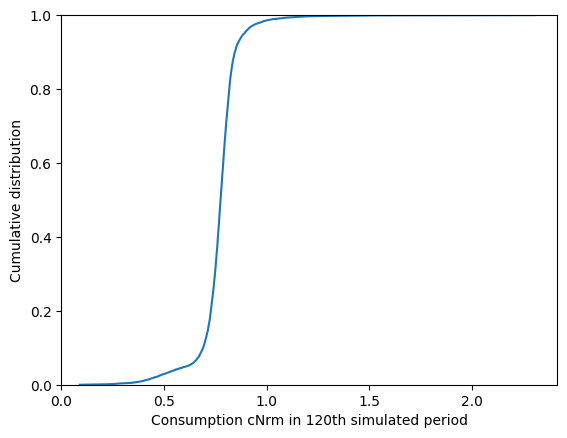
CDF = np.linspace(0.0, 1, N)
plt.plot(np.sort(LaborIntMargExample.controls["cNrm"]), CDF)
plt.xlabel(
r"Consumption $c_t$ in "
+ str(LaborIntMargExample.T_sim)
+ "th simulated period",
)
plt.ylabel("Cumulative distribution")
plt.xlim(0.0, None)
plt.ylim(0.0, 1.0)
plt.show()
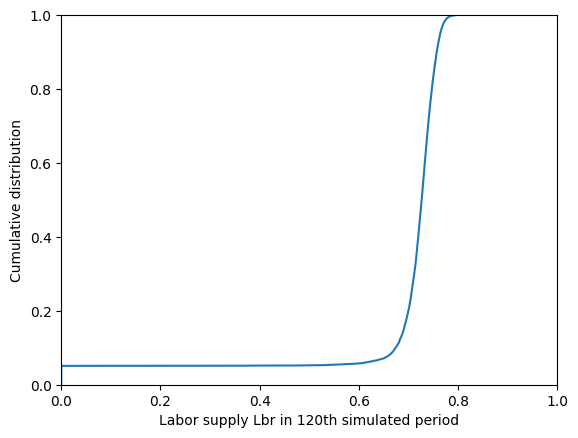
plt.plot(np.sort(LaborIntMargExample.controls["Lbr"]), CDF)
plt.xlabel(
r"Labor supply $\ell_t$ in "
+ str(LaborIntMargExample.T_sim)
+ "th simulated period",
)
plt.ylabel("Cumulative distribution")
plt.xlim(0.0, 1.0)
plt.ylim(0.0, 1.0)
plt.show()
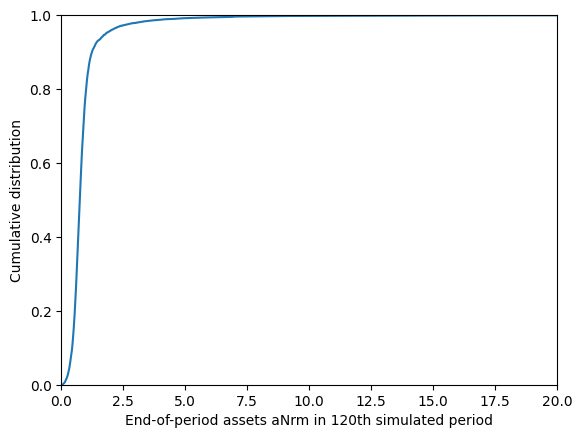
plt.plot(np.sort(LaborIntMargExample.state_now["aNrm"]), CDF)
plt.xlabel(
"End-of-period assets aNrm in "
+ str(LaborIntMargExample.T_sim)
+ "th simulated period",
)
plt.ylabel("Cumulative distribution")
plt.xlim(0.0, 5.0)
plt.ylim(0.0, 1.0)
plt.show()
Simulating 10000 intensive-margin labor supply consumers for 120 periods took 1.9375 seconds.
[12]:
# Make and solve a labor intensive margin consumer with a finite lifecycle
LifecycleExample = LaborIntMargConsumerType(**init_labor_lifecycle)
LifecycleExample.cycles = (
1 # Make this consumer live a sequence of periods exactly once
)
[13]:
start_time = process_time()
LifecycleExample.solve()
end_time = process_time()
print(
"Solving a lifecycle labor intensive margin consumer took "
+ str(end_time - start_time)
+ " seconds.",
)
LifecycleExample.unpack("cFunc")
Solving a lifecycle labor intensive margin consumer took 0.046875 seconds.
[14]:
bMax = 20.0
[15]:
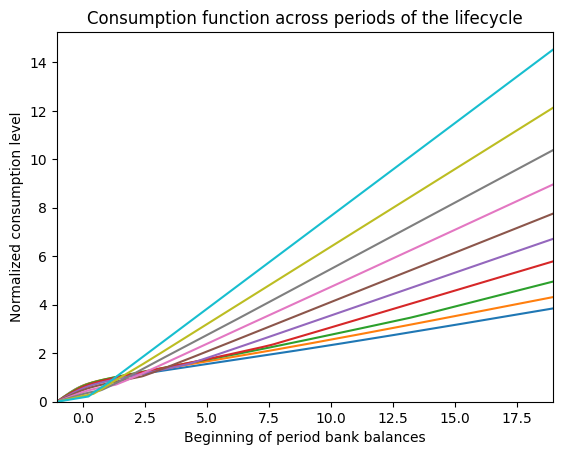
# Plot the consumption function in each period of the lifecycle, using median shock
B = np.linspace(0.0, bMax, 300)
b_min = np.inf
b_max = -np.inf
for t in range(LifecycleExample.T_cycle):
TranShkSet = LifecycleExample.TranShkGrid[t]
Shk = TranShkSet[int(len(TranShkSet) // 2)] # Use the median shock, more or less
B_temp = B + LifecycleExample.solution[t].bNrmMin(Shk)
C = LifecycleExample.solution[t].cFunc(B_temp, Shk * np.ones_like(B_temp))
plt.plot(B_temp, C)
b_min = np.minimum(b_min, B_temp[0])
b_max = np.maximum(b_min, B_temp[-1])
plt.title("Consumption function across periods of the lifecycle")
plt.xlabel("Beginning of period bank balances")
plt.ylabel("Normalized consumption level")
plt.xlim(b_min, b_max)
plt.ylim(0.0, None)
plt.show()
[16]:
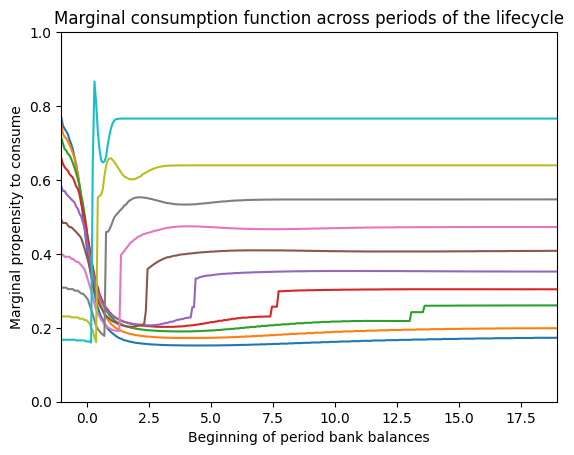
# Plot the marginal consumption function in each period of the lifecycle, using median shock
B = np.linspace(0.0, bMax, 300)
b_min = np.inf
b_max = -np.inf
for t in range(LifecycleExample.T_cycle):
TranShkSet = LifecycleExample.TranShkGrid[t]
Shk = TranShkSet[int(len(TranShkSet) // 2)] # Use the median shock, more or less
B_temp = B + LifecycleExample.solution[t].bNrmMin(Shk)
MPC = LifecycleExample.solution[t].cFunc.derivativeX(
B_temp,
Shk * np.ones_like(B_temp),
)
plt.plot(B_temp, MPC)
b_min = np.minimum(b_min, B_temp[0])
b_max = np.maximum(b_min, B_temp[-1])
plt.title("Marginal consumption function across periods of the lifecycle")
plt.xlabel("Beginning of period bank balances")
plt.ylabel("Marginal propensity to consume")
plt.xlim(b_min, b_max)
plt.ylim(0.0, 1.0)
plt.show()
[17]:
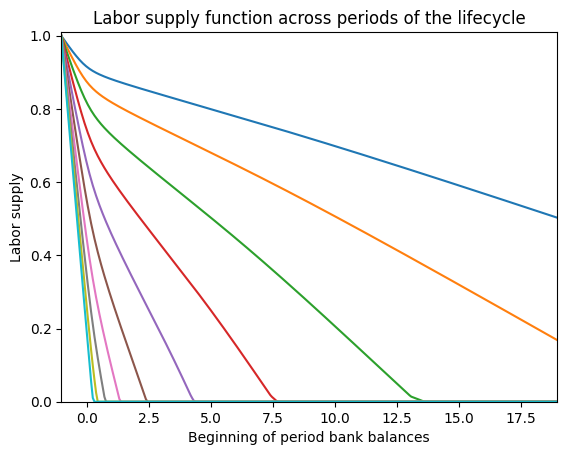
# Plot the labor supply function in each period of the lifecycle, using median shock
B = np.linspace(0.0, bMax, 300)
b_min = np.inf
b_max = -np.inf
for t in range(LifecycleExample.T_cycle):
TranShkSet = LifecycleExample.TranShkGrid[t]
Shk = TranShkSet[int(len(TranShkSet) // 2)] # Use the median shock, more or less
B_temp = B + LifecycleExample.solution[t].bNrmMin(Shk)
L = LifecycleExample.solution[t].LbrFunc(B_temp, Shk * np.ones_like(B_temp))
plt.plot(B_temp, L)
b_min = np.minimum(b_min, B_temp[0])
b_max = np.maximum(b_min, B_temp[-1])
plt.title("Labor supply function across periods of the lifecycle")
plt.xlabel("Beginning of period bank balances")
plt.ylabel("Labor supply")
plt.xlim(b_min, b_max)
plt.ylim(0.0, 1.01)
plt.show()
[18]:
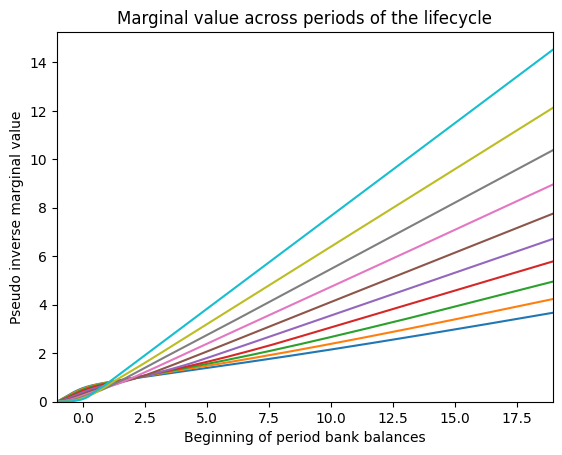
# Plot the marginal value function at various transitory productivity shocks
pseudo_inverse = True
TranShkSet = LifecycleExample.TranShkGrid[t]
B = np.linspace(0.0, bMax, 300)
b_min = np.inf
b_max = -np.inf
for t in range(LifecycleExample.T_cycle):
TranShkSet = LifecycleExample.TranShkGrid[t]
Shk = TranShkSet[int(len(TranShkSet) / 2)] # Use the median shock, more or less
B_temp = B + LifecycleExample.solution[t].bNrmMin(Shk)
if pseudo_inverse:
vP = LifecycleExample.solution[t].vPfunc.cFunc(
B_temp,
Shk * np.ones_like(B_temp),
)
else:
vP = LifecycleExample.solution[t].vPfunc(B_temp, Shk * np.ones_like(B_temp))
plt.plot(B_temp, vP)
b_min = np.minimum(b_min, B_temp[0])
b_max = np.maximum(b_min, B_temp[-1])
plt.xlabel("Beginning of period bank balances")
if pseudo_inverse:
plt.ylabel("Pseudo inverse marginal value")
else:
plt.ylabel("Marginal value")
plt.title("Marginal value across periods of the lifecycle")
plt.xlim(b_min, b_max)
plt.ylim(0.0, None)
plt.show()
[ ]: